Article • 13 min read
What is customer segmentation? Types, tips + strategy
Customer segmentation isn't just for marketing. Learn how to use it to deliver personalized and efficient support experiences your customers will love.
Kevin Boyer
Sr. Director, Product Marketing
Última actualización en August 7, 2025
Customer segmentation definitionCustomer segmentation is the process of grouping customers together based on shared traits, so businesses can market to them more effectively and provide a better, more personalized CX. Depending on your team’s goals, there are many ways you can segment your customers and connect with members of a certain group. It’s best to determine what they have in common—whether that’s a geographic location, career, or hobby. You can also organize by behavior (like buying habits) or demographics (like age or gender). No matter how you separate your customers, segmentation enables you to meet their needs and boost retention. |
You see it in office lunchrooms, at high school dances, and on the internet: People love belonging to groups. In the business world, grouping customers—or customer segmentation—offers valuable insight that allows you to customize your customer experience and build relationships with buyers.
But before you can start tailoring your customer support, you need to know how to organize customers in meaningful ways. Consider this your invitation to the table, where we’ll walk through the what, why, and how of effective customer segmentation.
More in this guide:
- Benefits of customer segmentation
- Comparing customer segmentation vs. market segmentation
- What are the types of customer segmentation?
- Segmenting customers effectively
- Key steps to building a customer segmentation strategy
- Frequently asked questions
- Successfully segment your customers with Zendesk
Benefits of customer segmentation
Treating all customers the same might seem efficient, but it often leads to missed opportunities and frustrated buyers. Segmenting your customers brings structure to the chaos, helping you serve the right people in the best way.
Here are a few key ways segmentation can improve your customer experience strategy.
Boosts marketing efforts
Customer segmentation allows you to craft more relevant marketing campaigns that speak directly to each audience’s needs. When you customize messaging to reflect a group’s specific priorities and behaviors, it’s far more likely to resonate and drive engagement.
For example, say you identify a sizable group of customers who left a competitor because they wanted a particular product feature that only you offer. This type of information is gold for your marketing team. It helps them get incredibly specific with both their messaging and their recipient list.
Provides faster support
Segmentation also streamlines the support experience, allowing agents to resolve issues more quickly.
When a segmented customer makes contact, the agent already has the information they need to immediately tackle the problem. AI-powered customer service tools can automatically capture details from the customer’s initial query and compare it to similar issues reported by other customers in the same segment, helping agents find solutions faster.
Customer segmentation also helps connect customers with the right agent the first time, minimizing frustrating transfers. For instance, agents focused on one product line or customer type are familiar with the issues commonly encountered in that group, so they can answer questions quickly and thoroughly.
Builds customer loyalty and lifetime value
Customer segmentation allows you to tailor your support experiences to the needs of certain groups. This shows buyers that you care about them and understand them, leading to increased satisfaction and engagement.
For instance, a retailer might identify a customer segment that frequently purchases seasonal products. By anticipating their needs and providing exclusive early access to new seasonal items, the retailer makes customers feel valued and understood. This encourages them to choose that retailer first and make repeat purchases year after year.
Offers greater personalization
Segmentation gives your team the context they need to personalize service to each group’s specific goals and expectations, and AI makes it easier to do this efficiently and at scale. For example, AI can use segmentation data to automatically surface onboarding tips for first-time customers, creating a helpful experience from the start.
According to Zendesk Benchmark data, 70 percent of customers expect personalization when interacting with a business. Meeting that expectation means going beyond surface-level gestures to deliver support that feels relevant and aligned with each customer’s unique situation.
Comparing customer segmentation vs. market segmentation
While they’re closely related, market segmentation and customer segmentation serve different purposes and focus on different audiences.
- Market segmentationis about dividing the entire potential market into distinct groups to identify and attract new customers. It helps inform product development, positioning, and marketing strategies aimed at your broader target audience, including people who haven’t bought from you yet.
- Customer segmentation focuses specifically on your existing buyers. You can use this data to attract new customers, but it’s also helpful when you’re trying to retain customers and build customer loyalty.
Customer segmentation can also reveal patterns and opportunities that help optimize internal operations, from prioritizing support resources to informing upsell strategies. It’s a critical step in understanding not just who your customers are, but how to serve them better.
What are the types of customer segmentation?
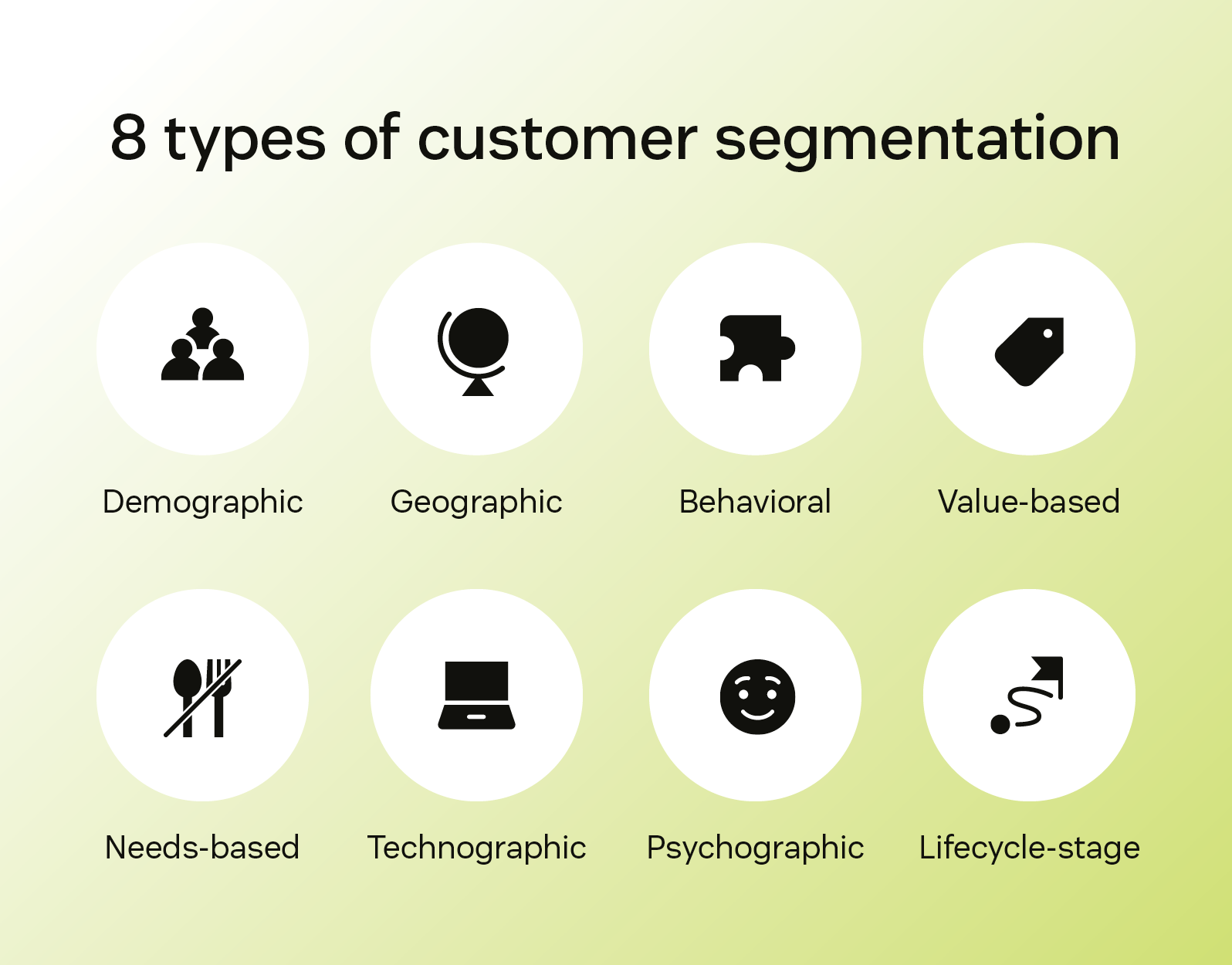
There’s not a universal segmentation method that’s equally meaningful for all businesses. You need to look at the data and see which customer segmentation model makes sense for your customers, employees, and business.
Many companies sort their audience based on eight types of customer segmentation.
1. Demographic segmentation
Demographic segmentation separates customers by basic identifiers, like:
Gender
Age
Income
Education
Marital status
This is helpful for marketing teams, who can use demographic data to personalize their messaging for customers in a particular group. Similarly, support teams can use these insights to adjust how they communicate with different demographics.
Example of demographic segmentation If you’re conversing with a Gen Z shopper on Instagram, break out the emojis. If you’re sending a baby boomer an email, you’ll likely use full sentences and a formal tone. |
2. Geographic segmentation
Geographic segmentation involves grouping customers based on where they live or work. This includes:
- Location: Customers are grouped by where they are (country, state, city).
- Language: Customers are grouped by the language they speak.
- Transportation: Customers are grouped by the transportation methods available in their area.
- Climate: Customers are grouped by the climate of the area (desert, rainy, snowy).
- Workplace: Customers are grouped by where they work (on-premise, work from home, hybrid).
This type of segmentation can help you tailor your product development, sales strategy, and marketing tactics for certain customer groups.
Example of geographic segmentation Imagine you own an online clothing store and want to sell winter coats and clothing. Customers in Ohio—where the winter weather is harsh—will have different needs and preferences than customers in San Diego. So, you’ll want to target your products and marketing efforts accordingly. |
3. Behavioral segmentation
Behavioral segmentation divides customers according to how they interact with your brand. This type of customer segmentation entails:
Purchasing frequency and timing
Response to promotions or offers
Product usage
Leveraging this information through customer segmentation analysis can help you enhance your offerings and customer service. For instance, if analysis reveals that a certain customer group consistently uses an advanced filter option, it may signal an opportunity to make that feature easier to find.
Behavioral data can also reveal which customers are more likely to upgrade or respond to special offers. When you know which customers are more likely to make repeat purchases or upgrade their plan, you can focus your cross-selling and upselling efforts on those segments.
Example of behavioral segmentation Rewards programs, like a simple “Buy 10, Get One Free” stamp card, show which customers buy frequently. You can then target frequent buyers with special offers or early access to new products |
4. Value-based segmentation
This type of segmentation groups customers based on the lifetime value they provide to your business, so you can allocate support resources where they’re needed most. If a certain type of customer isn’t generating a lot of revenue, you may want to rethink the level of support you’re offering them.
This allows your team to find cost-saving alternatives—such as self-service options—for lower-revenue-generating customers so your agents can spend more time helping higher-value customers. These clients are also far more likely to have complicated support issues that a help center or chatbot can’t solve.
Example of value-based segmentation Say a small business is calling your support team two or three times a month. Maybe you know the cost per unit for a phone call is $45, and your small-business clients pay only $15 for the product. You might want to take a closer look at phones as an unlimited channel for that customer segment. |
5. Needs-based segmentation
Needs-based segmentation is the process of grouping customers who have similar and specific requirements for products and services. Oftentimes, the customers are grouped by shared experiences, and the company aims to learn their pain points, problems, wants, or needs.
- Product needs: Some customer groups require certain features; otherwise, they won’t use your products.
- Service needs: Customers expect and want particular services when interacting with your business.
Example of needs-based segmentation If a segment of your customers follows a vegan diet, identifying them as a distinct group with specific dietary needs lets you cater to that group accordingly. By adding a few vegan options, you not only meet their expectations but also build loyalty with that segment. |
6. Technographic segmentation
Technographic data tells you how familiar and comfortable customers are with technology. It also indicates what types of technology they prefer to use. The best way to gather this information is through customer surveys.
Technographic segmentation is particularly useful for software as a service (SaaS) companies that develop new products that can work well with other solutions.
7. Psychographic segmentation
Psychographic segmentation separates customers into groups according to their:
Personalities
Opinions
Values
Lifestyle
Attitudes
Interests
This type of customer segmentation is among the most effective, as it allows marketing teams to get a glimpse into customers’ thoughts and perceptions and how they feel about companies’ products and services. You can use this data to craft a brand personality that aligns with your customers’ psychological characteristics.
Customer surveys—like CSAT and NPS—can provide first-hand information and vital feedback that help you gather insights and identify what drives their buying behaviors.
Example of psychographic segmentation Say you sell handcrafted jewelry, which often comes with a higher price tag. You can use psychographic segmentation to identify customers who can afford to spend money on luxury goods—and enjoy doing so. |
8. Lifecycle stage segmentation
This segmentation model involves grouping customers based on where they are in the customer journey. It highlights how customers’ support needs change as they move through different stages of their lifecycle.
For example, instead of asking basic questions on how to use your product, veteran users will ask questions to help them maximize your product’s efficiency.
Lifecycle segmentation is especially important with long-term B2B customers. These clients are likely to continue growing the longer they stay with your company, meaning their support needs will change, too. B2B customers tend to rely heavily on customer serviceto help their businesses expand.
Example of lifecycle stage segmentation Customers often need a lot of support during the onboarding process. By segmenting customers in this early stage, your team can proactively offer check-ins, tutorials, or fast-track support—then gradually scale back as they become more self-sufficient. |
Segmenting customers effectively
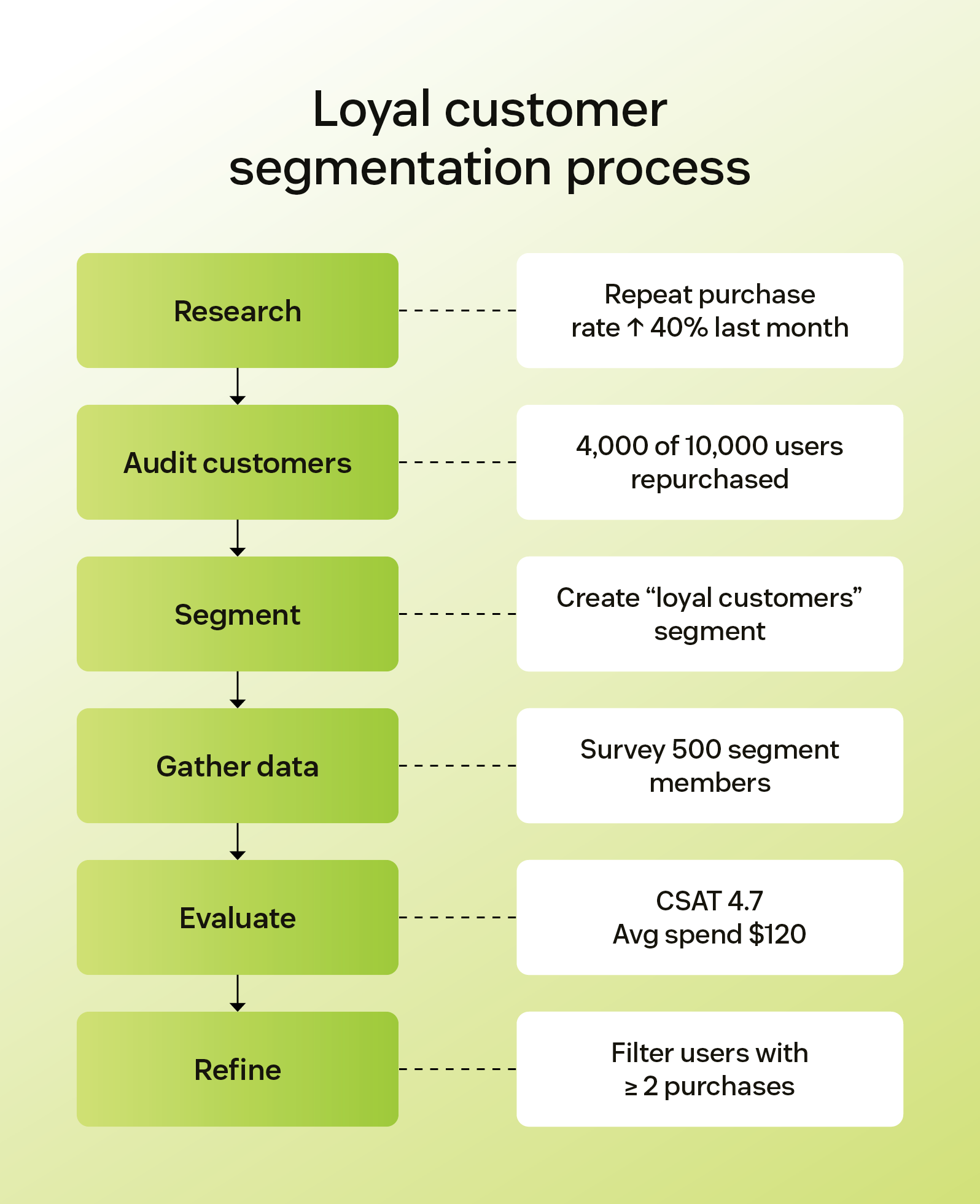
To keep up with fast-changing customer expectations, you need up-to-date data and a clear segmentation strategy. Here’s how to get started:
- Do industry and market research:Identify trends and common customer needs within your industry.
- Examine your current customer base: Look for patterns in behavior, preferences, or value that can inform useful segment types for your company.
- Adopt a customer segmentation tool: Integrating an AI-powered tool like Zendesk can help you group customers and track data efficiently.
- Gather customer experience data:Collect feedback and usage data through surveys, analytics tools, or your CRM.
- Evaluate the data: Analyze the data to identify trends and opportunities in your segments.
- Refine your customer segments:Adjust criteria as needed to stay aligned with customer needs and business goals.
Key steps to building a customer segmentation strategy
Your customer segmentation strategy is your roadmap to how and why you’re organizing your audience. This plan should describe the reasons you’re using segmentation, the model you’re choosing, and the ways in which you’ll measure success.
- Determine your goals: Identify what you want segmentation to achieve for both your business and customers.
- Identify the best way to segment your customers: Decide which segmentation method best supports your goals. If applicable, start with models used by other teams or create support-specific segments based on key traits like company size or behavior.
- Target and reach your customer segments: Start by developing customer personas to clearly define who you’re targeting within each segment. Then personalize how you reach them to meet their unique needs and expectations.
- Revisit your strategy regularly: Review your approach often and make changes as needed. Finding the groupings that work best might take some time, but don’t give up.
- Collect and analyze feedback: Use data like customer surveys, support conversations, and CSAT scores to improve segmentation and deliver better experiences.
Frequently asked questions
Customer story


LimeBike
LimeBike scales through high-growth cycles with Zendesk
“There’s not really anything on the market that I can think of that compares to Zendesk. I’m really happy with what we have—Zendesk gives me everything I need to effectively manage my team. The tools that Zendesk provides helps LimeBike to be the leading smart mobility solution provider with happy riders.”
- Lakeysha Hayes
Domestic and International Customer Service Manager
Successfully segment your customers with Zendesk
Segmentation is only as powerful as the tools behind it. Zendesk helps you turn strategy into action with detailed customer profiles that give your team the full picture, all in one place.
With AI purpose-built for CX, Zendesk for customer service enables personalized, context-aware support at scale. Whether you’re identifying high-value customers or tailoring support based on lifecycle stage, Zendesk makes it easier to serve the right customer in the right way—every time.

